Naval ships broken at Wards 1965-1970
| < 1962-1964 | Δ Index | 1971 > |

1965
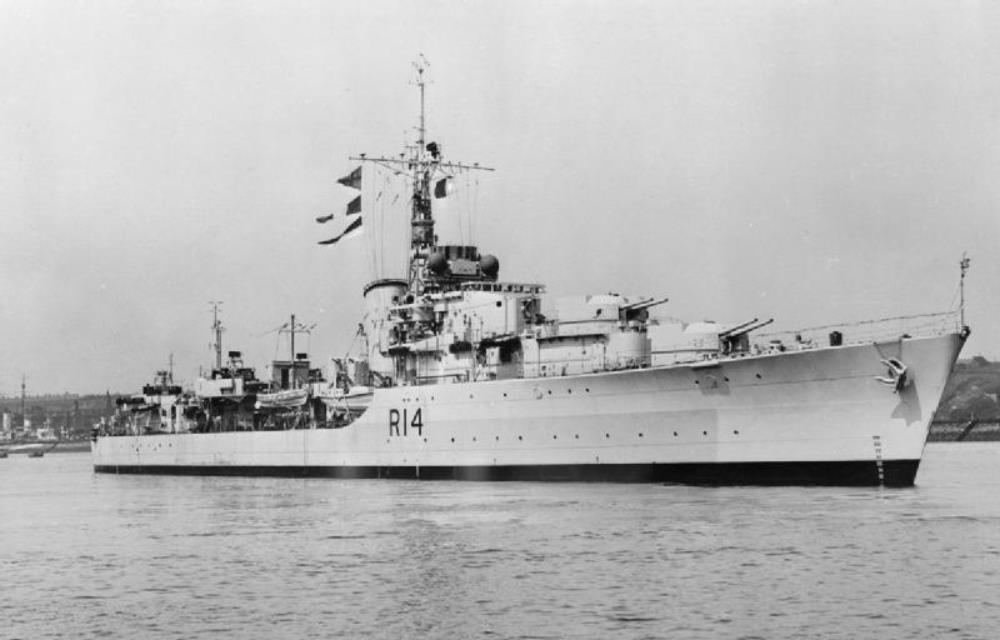 HMS Armada
HMS Armada
HMS Armada – a Battle-class destroyer, built by Hawthorn Leslie and Company, Tyneside, launched 9th December 1943, commissioned 2nd July 1945.
Joined the British Pacific Fleet but did not see action during the Second World War. In 1946 deployed to the Far East, performing a variety of duties while based there. Returned to the UK in 1947, and was placed in Reserve.
In 1949, Armada deployed to the Mediterranean as part of the 3rd Destroyer flotilla. In 1956, Armada was in the area during the Suez crisis.
In 1960, Armada was decommissioned, and in 1965, she was sold to Thos W Ward for scrapping at Inverkeithing.
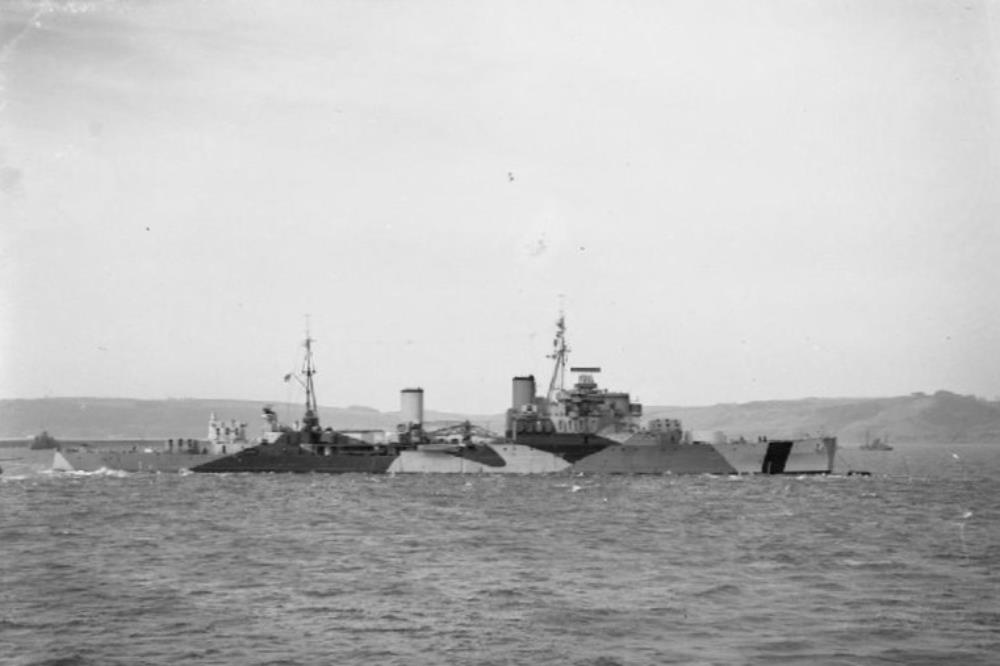 HMS Mauritius
HMS Mauritius
HMS Mauritius – Crown Colony-class light cruiser, built by Swan Hunter, Tyne and Wear, launched 19th July 1939, commissioned 4th January 1940.
She joined the Eastern Fleet in 1942, but was withdrawn in April 1943 to reinforce the Mediterranean Fleet participating in the landings in Sicily, and as a unit of Support Force East, when she carried out shore bombardment duties.
In September she was part of the covering force for the Salerno landings, then carried out anti-blockade-runner patrols in the Bay of Biscay. She returned to the Mediterranean, for the Anzio landings, in January 1944.
In June 1944 she covered the landings in Normandy off Sword Beach, then carried out offensive patrols of the Brittany coast in August to mop up German shipping in the area. After this she returned to the Home Fleet, covering the carrier raids along the Norwegian coast and making anti-shipping strikes.
In 1946 she served in the Mediterranean, returning to the UK in 1948. After a spell in reserve and in refit, she recommissioned in 1949 for the 1st Cruiser Squadron in the Mediterranean, sailing on 6 May 1949. From 1949 to 1951 she was on the East Indies Station before returning to the UK.
Mauritius was placed in reserve in 1952 and remained there until she was sold to Thos W Ward., arriving at Inverkeithing, on 27 March 1965.
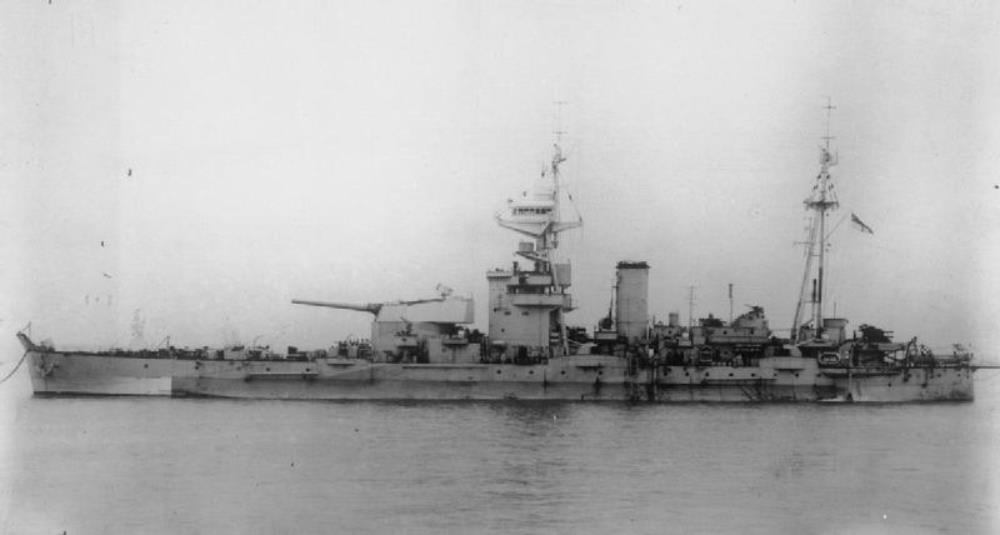 HMS Roberts
HMS Roberts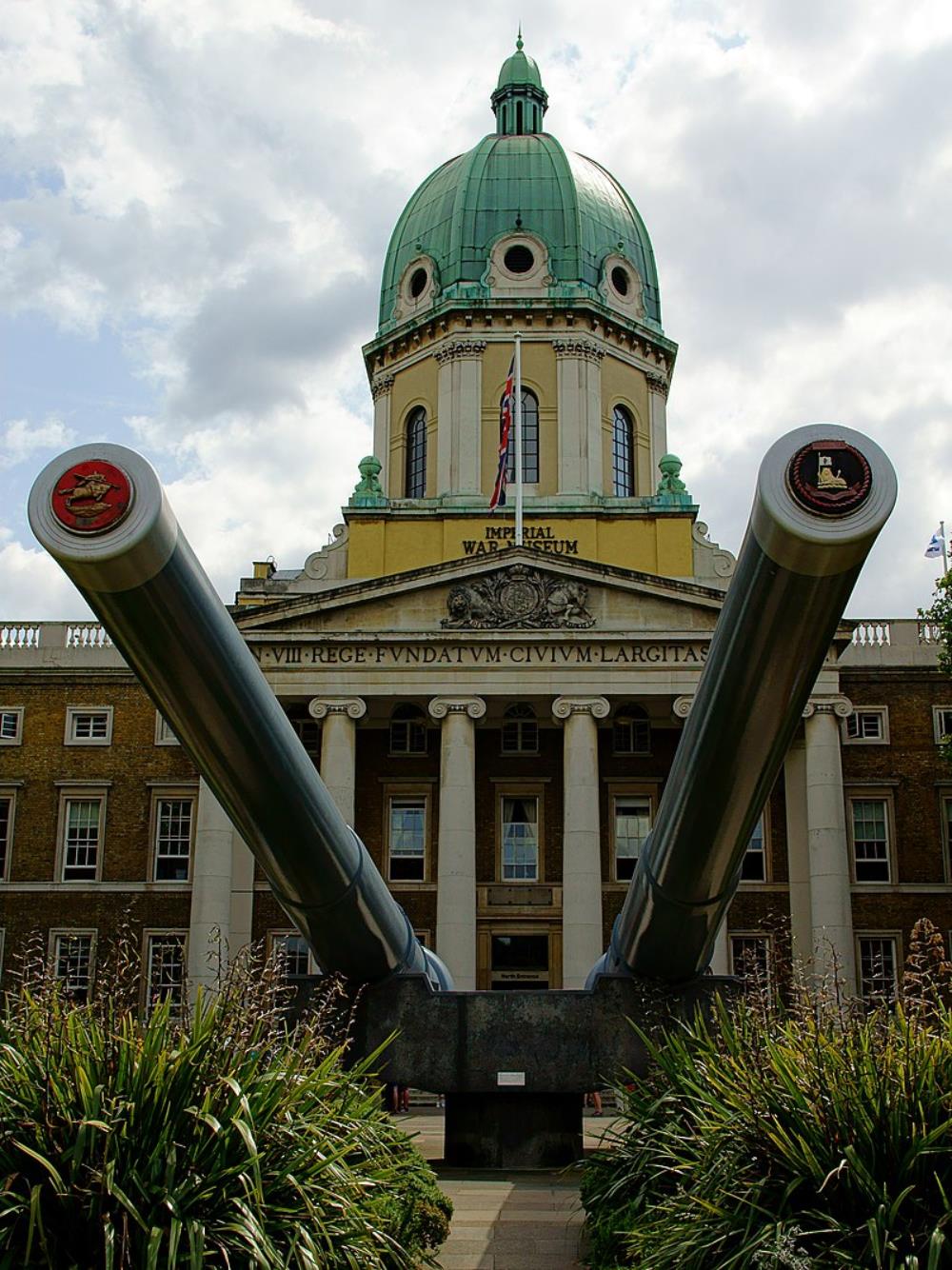 One of Roberts’ guns (originally in the battleship Resolution) is mounted outside the Imperial War Museum in Lambeth, south London, together with one from the battleship Ramillies.
One of Roberts’ guns (originally in the battleship Resolution) is mounted outside the Imperial War Museum in Lambeth, south London, together with one from the battleship Ramillies.
HMS Roberts – a Roberts-class monitor, built by John Brown & Company, Clydebank, launched 1st February 1941, commissioned 27th October 1941. She reused the twin 15-inch gun turret of the First World War monitor Marshal Soult.
Roberts provided bombardment support during Operation Torch in North Africa, the invasion of Sicily and the Allied landings near Salerno. During the D-Day landings, she was controlled from the headquarters ship HMS Largs positioned off Sword beach
In July 1945, Roberts departed the United Kingdom for the Indian Ocean to support Operation Mailfist, the planned liberation of Singapore. She was near Port Said at the time the Japanese surrender on 15 August, but was not recalled until 11 September by which time she had reached Kilindini Harbour in Kenya. She eventually reached Plymouth on 22 November.
Roberts was sold for scrap shortly after the war, but hired back by the navy as an accommodation ship at Devonport until 1965.
She was sold for scrap again in July 1965, finally berthing at Inverkeithing for break up in early August.
1967
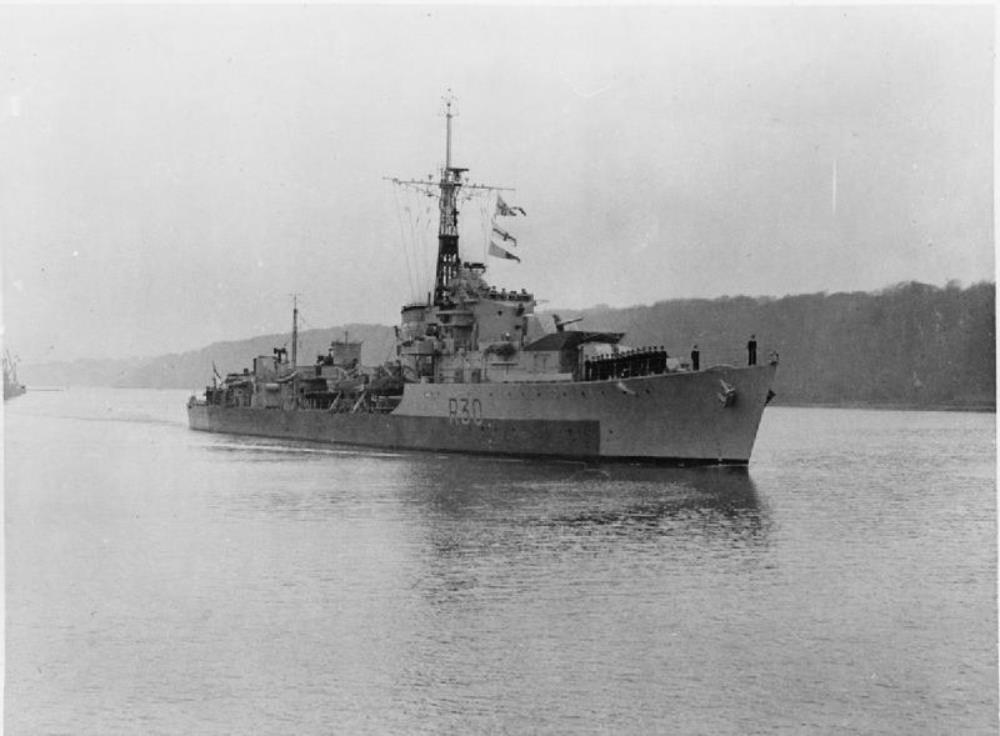 HMS Carron
HMS Carron
HMS Carron – a C-class destroyer, built by Scotts, Greenock, (originally named Strenuous, renamed Carron before being) launched on 28th March 1944. Commissioned 28th July 1944.
Allocated to the 6th Destroyer Flotilla for service with the Home Fleet. After a refit in mid-1945 to augment her anti-aircraft armament, she was transferred for service in the Far East in June, but joined the East Indies Fleet at Trincomalee, British Ceylon, in August.
Following the war Carron was paid off into reserve. She was the first of her class to be selected for modernisation. Work included a new bridge and gunnery fire control system, as well as the addition of Squid anti-submarine mortars.
She emerged from modernisation in 1955 for service with the Dartmouth Training Squadron. In 1960 the ship was further de-equipped so she could serve as a navigational training ship, with only her torpedo tubes remaining and further charthouses fitted on the Squid deck.
Carron was paid off on 5 April 1963 and was listed for sale on 30 May. She was sold for scrap to Thos W Ward arriving at Inverkeithing on 31 March 1967.
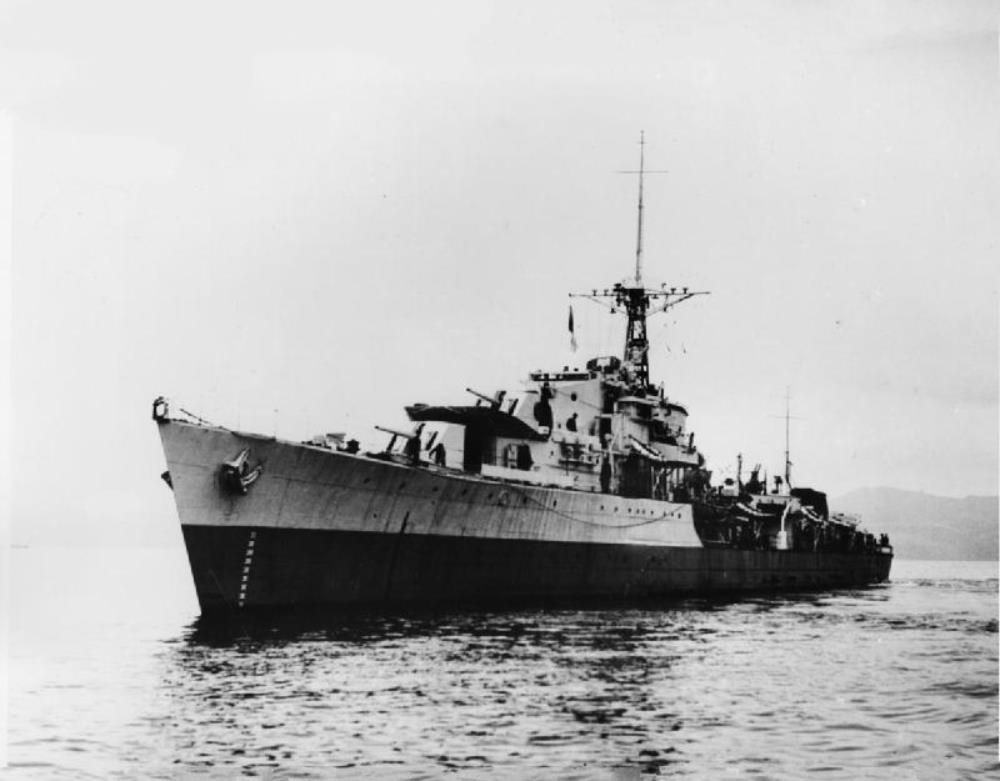 HMS Cassandra
HMS Cassandra
HMS Cassandra – a C-class destroyer built by Yarrow Shipbuilders, Scotstoun, launched 29th November 1943, commissioned 28 July 1944. (She was originally to be named HMS Tourmaline but this was changed to Cassandra in November 1942 to fit her revised class name.)
After commissioning, she escorted Russian convoys and was engaged in the search for the German battleship Tirpitz2]
After the war, she was placed in reserve in 1946. She then served in the Mediterranean Sea and Indian Ocean before being modernised.
She re-entered service in April 1960 in the Far East as part of the 8th Destroyer Squadron. In late June 1961, Cassandra was sent to the Persian Gulf in response to Iraqi threats to annex Kuwait, before return to the Far East. In 1964 and 1965 she served in the Mediterranean and the Far East, including service in the Indonesian Confrontation.
The destroyer was placed in reserve until paying off in January 1966.
Cassandra arrived at the breaker’s yard of Thos W Ward at Inverkeithing for scrapping on 28 April 1967.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Cassandra_(R62)
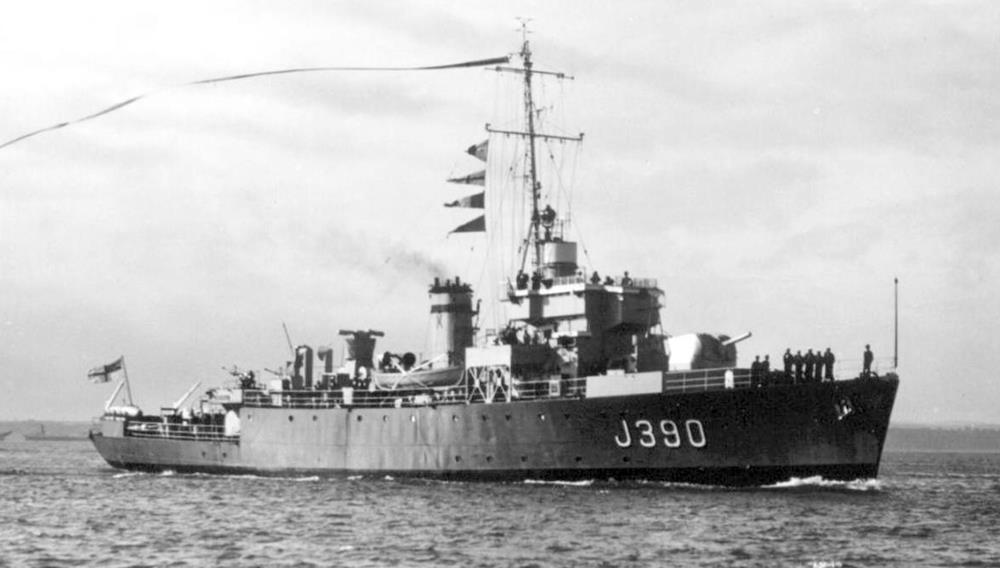 HMS Jewel
HMS Jewel
HMS Jewel – an Algerine-Class Minesweeper built by Harland and Wolff, Belfast, launched 20th July 1944, commissioned 9th December 1944.
Joined 10th Minesweeping Flotilla, and spent the remainder of WW2 on minesweeping duties in the North Sea, clearing paths through British minefields to give easier access to Scapa Flow, and clearing German minefields in the North Sea, and mines dropped by German aircraft in the English Channel.
In June 1945 she was refitted at Antwerp prior to mine clearance in areas near Singapore including ports in Indonesia and Hong Kong.
She was reduced to reserve status in September 1946. In 1948 she became the Drill Ship for the RNVR at Dundee.
In 1955 she was refitted at Devonport before recommissioning r for service in the Dartmouth Training Squadron.
She was deployed for training of Cadets from the Royal Naval College at Dartmouth until 1961 when she again Paid-off and was placed in Reserve. In 1966 she was sold Thos. Ward, arriving at Inverkeithing on 7 April 1967.
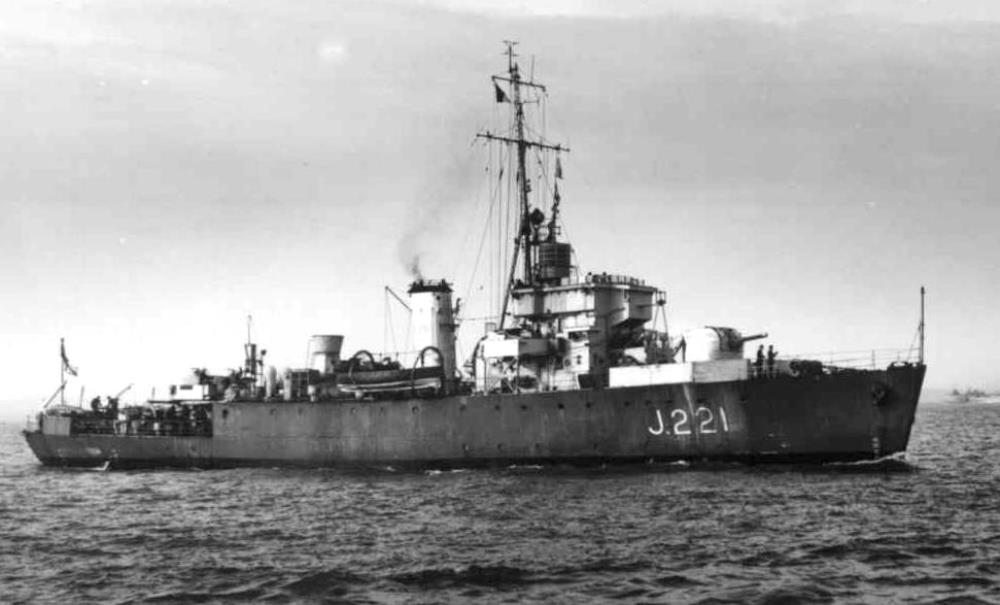 HMS Onyx
HMS Onyx
HMS Onyx – an Algerine-Class Minesweeper built by Harland and Wolff, Belfast, launched 27th October 1942 commissioned 26th March 1943.
Joined 18th Minesweeping Flotilla, minesweeping in North-western approaches, then in English Channel and North Sea. December 1943, anti-submarine patrols off Scapa Flow. January 1944, North western approaches and Arctic convoys on approach to Loch Ewe. May 1944 minesweeping in English Channel prior to D-day landings
Autumn 1944 to August 1945 minesweeping in English Channel and off French, Belgian and Dutch coasts.
After VJ Day the ship was refitted then deployed to SW Approaches and Bristol Channel.
In March 1947 she was transferred to the 3rd Flotilla at Port Edgar then Paid-off and was reduced to Reserve status in August 1947. She was moved to the Reserve Fleet Plymouth where she remained until she was sold to Thos. Ward, arriving at Inverkeithing on 5th April 1967.
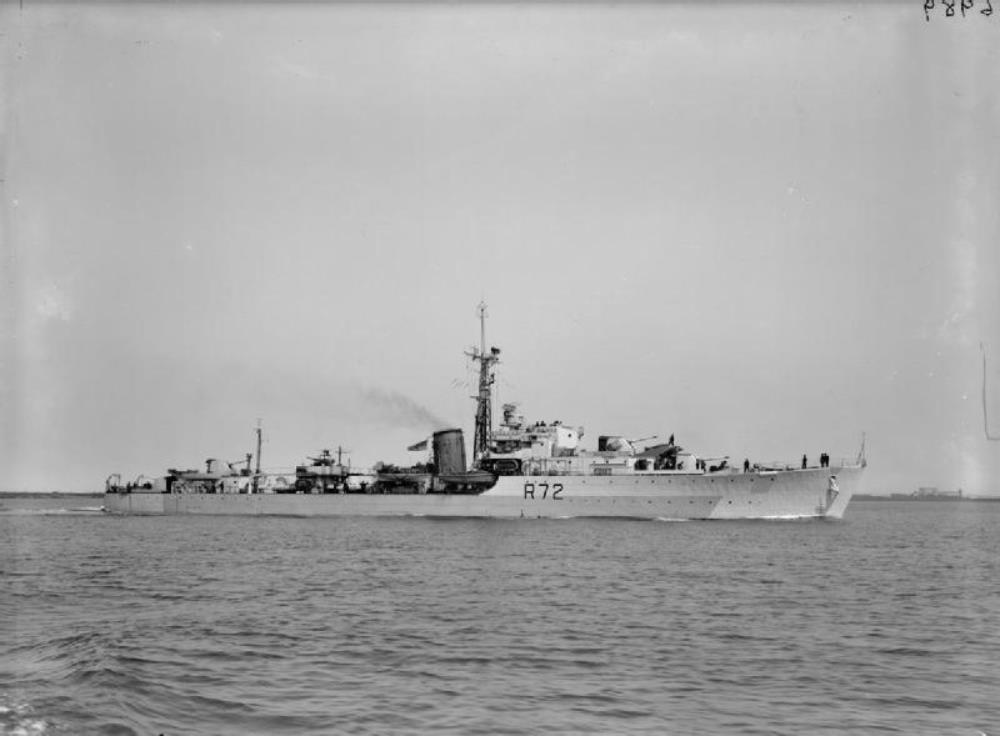 HMS Wizard
HMS Wizard
HMS Wizard – W-class destroyer built by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow-in-Furness, launched 29th September 1943, commissioned 30 March 1944.
Assigned to screen aircraft carriers Furious and Searcher until 9 June 1944, when she was damaged by an explosion of her own depth charges. After repairs she was assigned to the British Pacific Fleet arriving after the surrender of Japan on 2 September 1945.
From 1946 until 1951 Wizard served in the Plymouth local flotilla. During 1953 and 1954 she was converted into a Type 15 fast anti-submarine frigate.
In 1956 Wizard deployed to the eastern Mediterranean as part of the Royal Navy force which took part in the Suez Crisis. On return to UK in May 1957 she refitted at Chatham before joining the Dartmouth Training Squadron for two years before being deployed in the West Indies with the 8th Frigate Squadron until 1964. On return she resumed Cadet training and remained with the Dartmouth Squadron until 1966.
In 1966 she was paid-off and was reduced to Reserve status, then sold to Thos W arriving at Inverkeithing on 7 March 1967.
1968
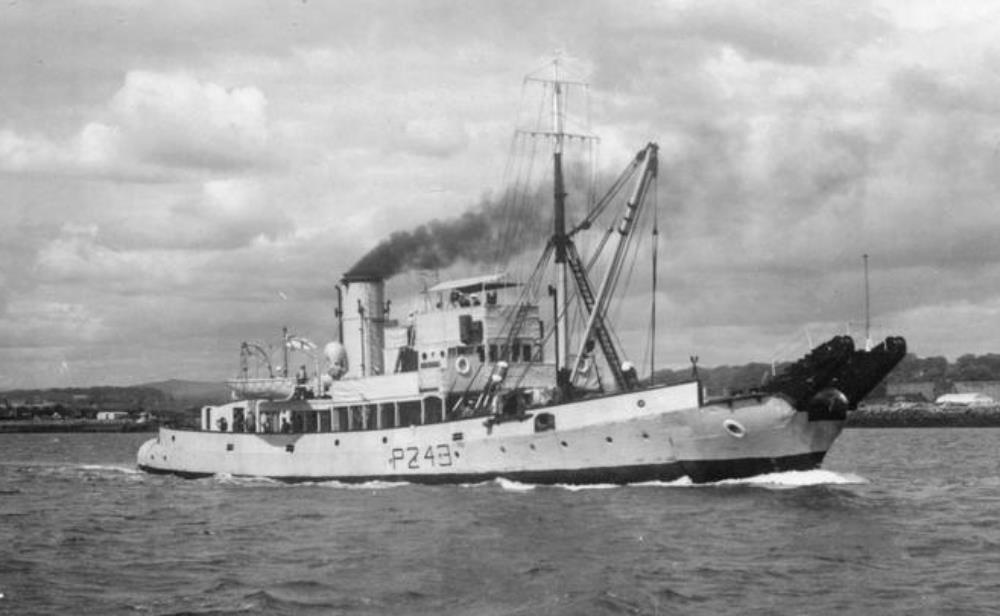 HMS Barbican
HMS Barbican
HMS Barbican – Bar-class boom defence vessel, built by Blyth Shipbuilding & Drydock Co. Ltd. Blyth, Launched 14th Mar 1938.
Wartime service history unknown
1950-1958 Her home port was Rosyth and went to the Med at the time of the Suez crisis but the Egyptians closed the canal and so she stayed at Valletta.
www.uboat.net
modelshipworld.com
www.forcesreunited.co.uk
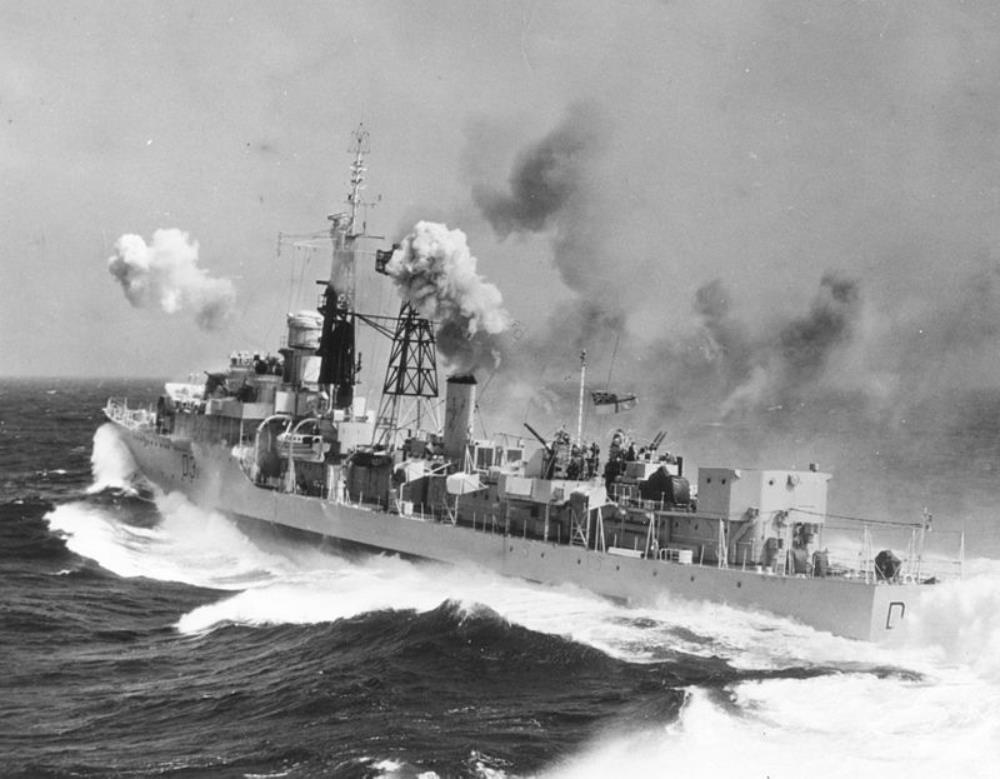 HMS Broadsword
HMS Broadsword
HMS Broadsword – a Weapon-class destroyer built by Yarrow Shipbuilders Ltd., Scotstoun, launched 4th February 1946, commissioned 4th October 1948.
Joined the 6th Destroyer Flotilla, as part of the Home Fleet, along with the other Weapon-class destroyers. In 1953 she went into reserve. In 1957 all of the Weapon class were taken into refit and conversion to re-equip them as radar pickets. Broadsword was converted at Rosyth. She re-commissioned in October 1958 to the 7th Destroyer Squadron serving in Home and Mediterranean waters until paying off in 1963.
Following decommissioning Broadsword was towed on 25 April 1968 to Rosyth for use in target trials.
She was sold to Thos. Ward and arrived at Inverkeithing on 8th October 1968.
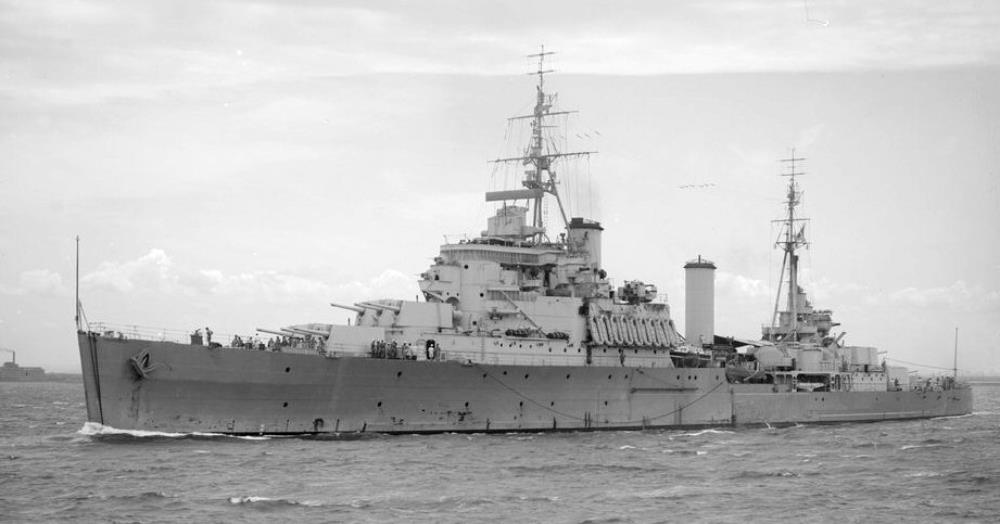 HMS Gambia
HMS Gambia
HMS Gambia – a Fiji-class light cruiser built by Swan Hunter, Tyne and Wear, launched 30th November 1940, commissioned 21st February 1942.
The cruiser saw active service in the East Indies with the British Eastern Fleet, and the Battle of Madagascar in September 1942. She then carried out trade protection duties in the Indian Ocean.
She transferred to the Royal New Zealand Navy on 22nd September 1943. In December, she commenced anti-blockade runner patrols in the Bay of Biscay pursuing the German blockade-runner Osorno. In 1944, she served with the British Pacific Fleet, participating in attacks on Japanese positions throughout the Pacific. In February she searched for blockade runners in the Cocos Islands area. She supported a series of carrier raids against oil installations and airfields, and saw action off Okinawa, Formosa and Japan, firing some of the last shots of WWII.
After a refit she was recommissioned on 1 July 1946 for the Far East Fleet. She returned to the UK on 6 January 1948, and in January 1950 was assigned to the Mediterranean. In 1953, she brought aid to the island of Zakynthos when it was struck by an earthquake.
In 1955 she became flagship of the 4th Cruiser Squadron on the East Indies Station, then had a refit in 1956.
In May 1957 Gambia sailed for the Persian Gulf, returning to Rosyth in September 1958. In 4 November 1958 she was back in the Mediterranean then the Far East in December 1959. She served the last months of 1960 in the South Atlantic before entering the reserve in December 1960.
Sold to Thos. W Ward, she arrived at Inverkeithing on 5th December 1968.
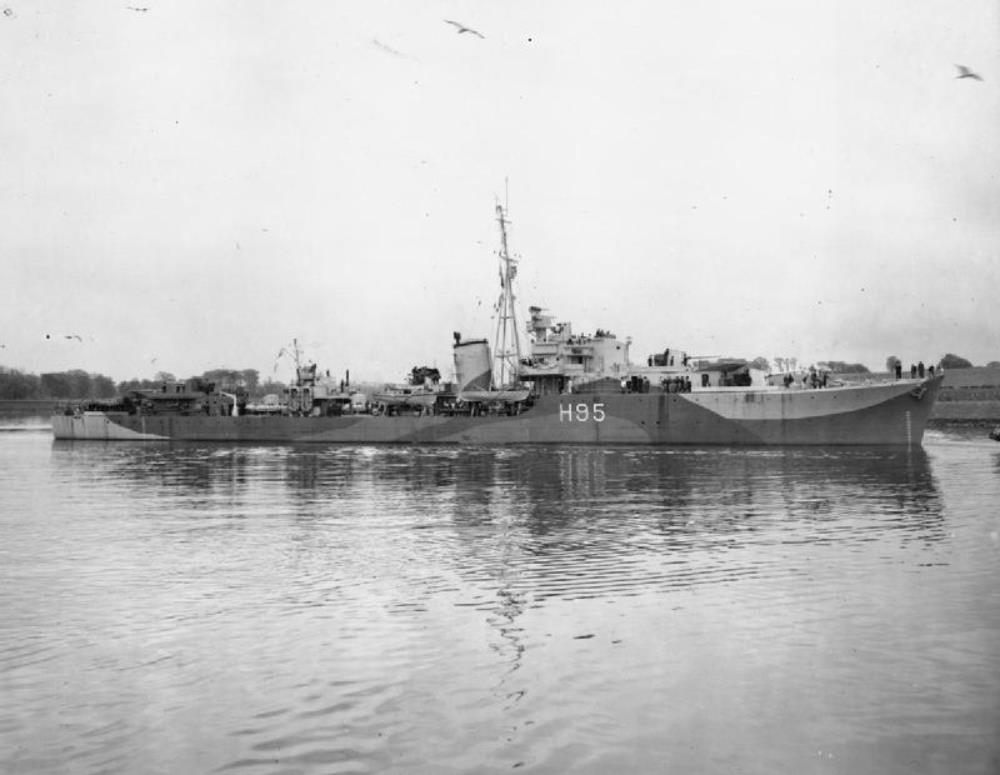 HMS Roebuck
HMS Roebuck
HMS Roebuck – an R-class destroyer, built by Scotts Shipbuilding & Engineering Co. Greenock, launched prematurely by an air raid on 10th December 1942 then salvaged and commissioned 10th June 1943.
In August 1943 she was deployed for convoy defence and patrols in the Indian Ocean. In 1944 she formed part of the escort for task force searching for the German U-Boat supply ship Brake.
In June 1944 she was deployed off Burma and bombarded Martaban.
In July she was part of the screen for major units against targets at Sabang and Sumatra
In 1945 she conducted patrols and bombarded the Cocos Islands before covering the landings at Rangoon, and attacks on Japanese ships.
In August Roebuck was preparing for large-scale landings but the surrender of Japan brought hostilities to a close
Roebuck returned to the UK for a refit. In 1952 she was converted to a Type 15 anti-submarine frigate, and joined the Mediterranean Fleet, serving until 1956 when she was placed in reserve. She went into refit again in 1959 and remained on the operational list until returning to reserve in 1962.
She was used for underwater explosion trials at Rosyth by the Naval Construction Research Establishment (NCRE), before being sold to Thos. W Ward arriving at Inverkeithing on 8th August 1968.
1969
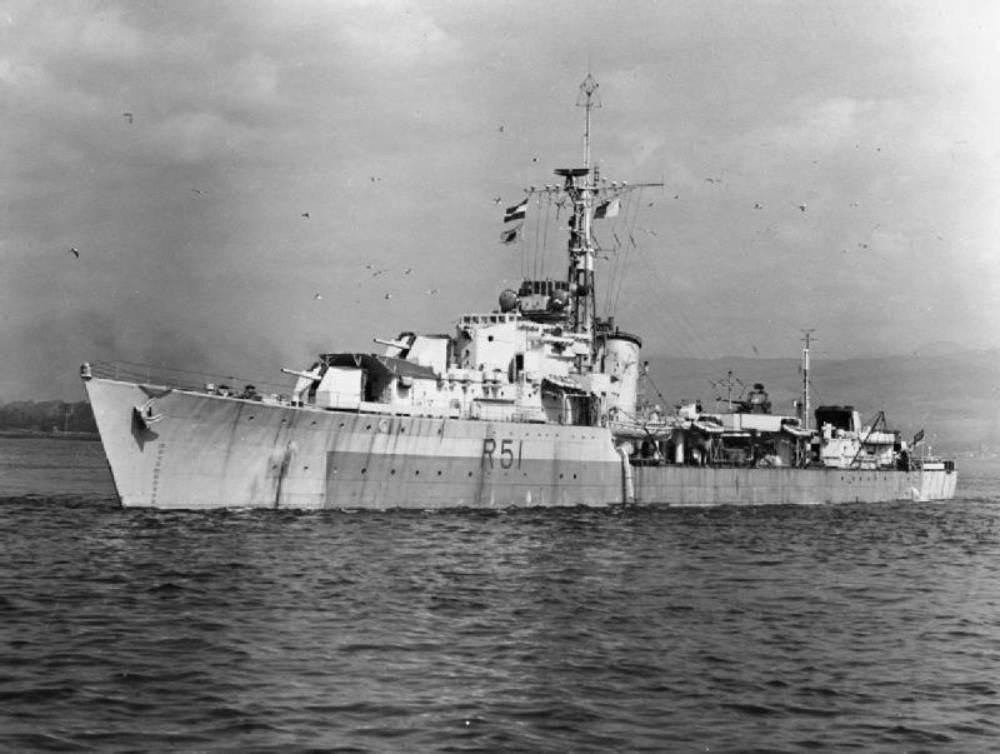 HMS Chevron
HMS Chevron
HMS Chevron – a C-class destroyer built by Alexander Stephen and Sons Limited, Linthouse, launched 23rd February 1944, commissioned 23rd August 1945, too late for service in WWII.
In December 1946, she was part of the ‘Palestine Patrol’, tasked with intercepting illegal Jewish immigration to Palestine. On 6 February 1952, she rescued 14 of the crew of a US aircraft that made a landing east of Cyprus. In 1954 Chevron returned to Portsmouth from the Mediterranean and decommissioned. In 1956 she was briefly recommissioned and served during the Suez Crisis. From 1957 until 1969 she served as an accommodation ship at Rosyth
She was sold to Thos W Ward arriving at Inverkeithing in December 1969.
Her bell is preserved at the Collingwood Area School, New Zealand.
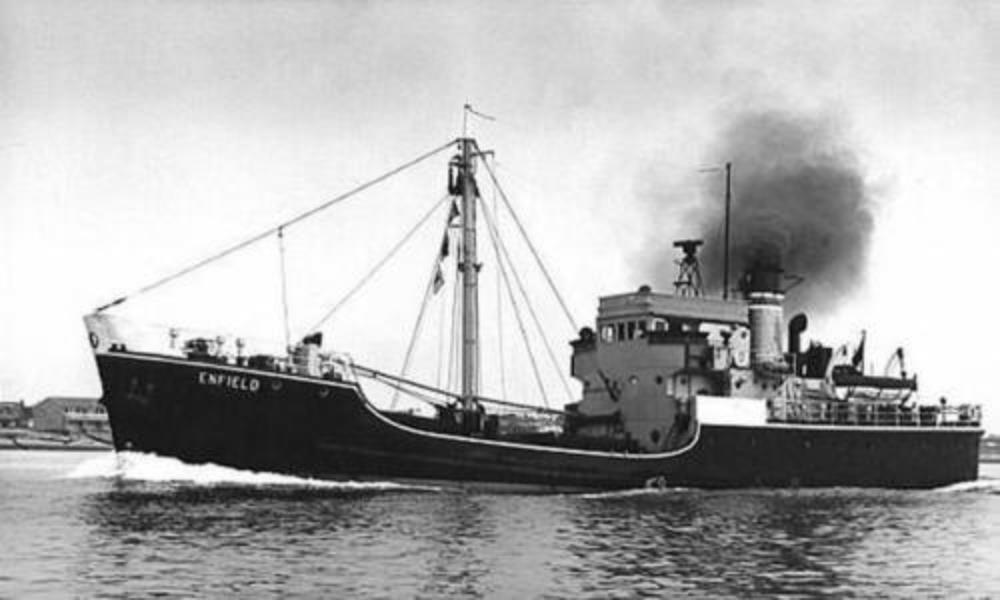 NAV Enfield
NAV Enfield
NAV Enfield – a Gatling class Armament Stores Carrier, built by Lobnitz & Co Ltd, Renfrew, Launched 5th September 1945.
The five Gatling-class ships were designed to carry ammunition ashore from larger ships as part of a 1943 plan for a future invasion of Japan. None was completed before the end of hostilities. Two were converted for mercantile use, with three completed for dockyard use.
Enfield operated out of Scotland serving Dundee, Crombie Fort William Corpach, Invergordon, Oban and Londonderry.
On 21 December 1948 while dumping old ammunition off May Island some exploded causing slight damage to the ship.
On 12 July 1953 she responded to an SOS from the motor yacht Owen Roe in thick mist off the Mull of Kintyre, rescued the crew and towed the ship to the Sound of Islay.
On 23 September 1969 she sold to Thos.W. Ward arriving at Inverkeithing in February 1970
www.historicalrfa.org
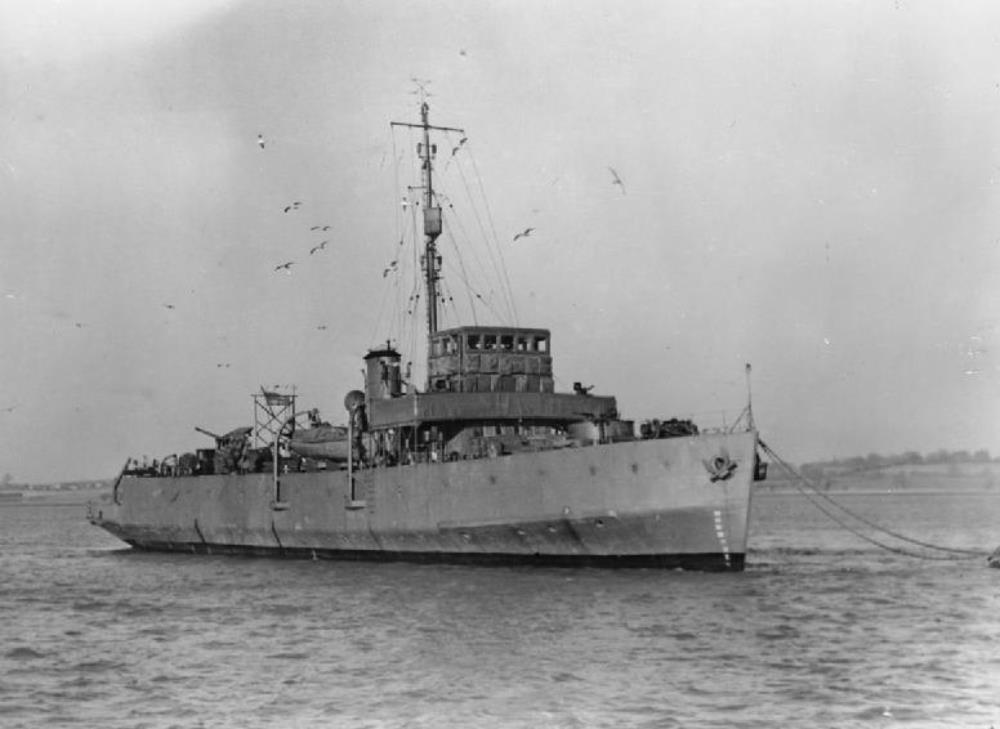 HMS Plover
HMS Plover
HMS Plover – a Coastal minelayer, built by William Denny and Brothers, Dumbarton launched 8th June 1937, commissioned 24th September 1937.
HMS Plover was intended to conduct mining trials and was therefore fitted to recover as well as lay mines. During World War II she laid a total of 15,237 mines, including two that sank the German destroyer Z8 Bruno Heinemann off the Belgian coast in January 1942.
Near the end of the war, the German submarine U-325 struck a mine that was part of a minefield laid by Plover on the morning of 30 April 1945
The ship was kept in service after the war. She was sold to Thos W Ward arriving at Inverkeithing in April
1970
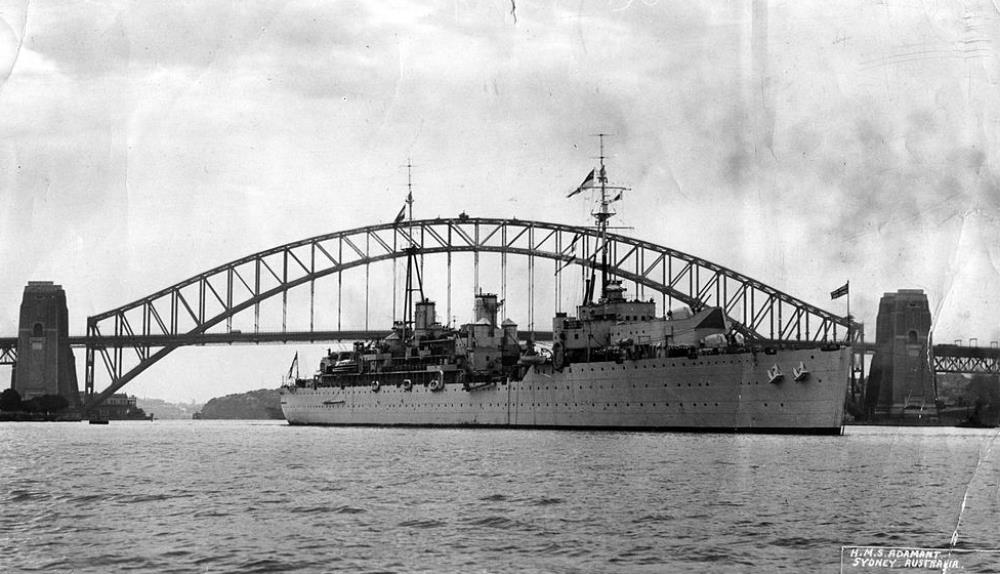 HMS Adamant
HMS Adamant
HMS Adamant – a Submarine depot ship, built by Harland and Wolff, Belfast, launched 30th November 1940, commissioned 28th February 1942.
She served in the Eastern Fleet (Colombo/Trincomalee) from April 1943 until April 1945 and then moved to Fremantle, Australia. In 1950, she returned to England, where she remained until 1954 as flagship of the Senior Officer, Reserve Fleet, Portsmouth
In October 1954, she was commissioned as depot ship to the 3rd Submarine Squadron at Rothesay, where she was based until October 1957. She then moved to Faslane from 1959 to 1962. In early 1964, she moved to Devonport. In March 1966 she was listed for disposal.
In September 1970 she arrived at Inverkeithing to be broken up.
wikipedia
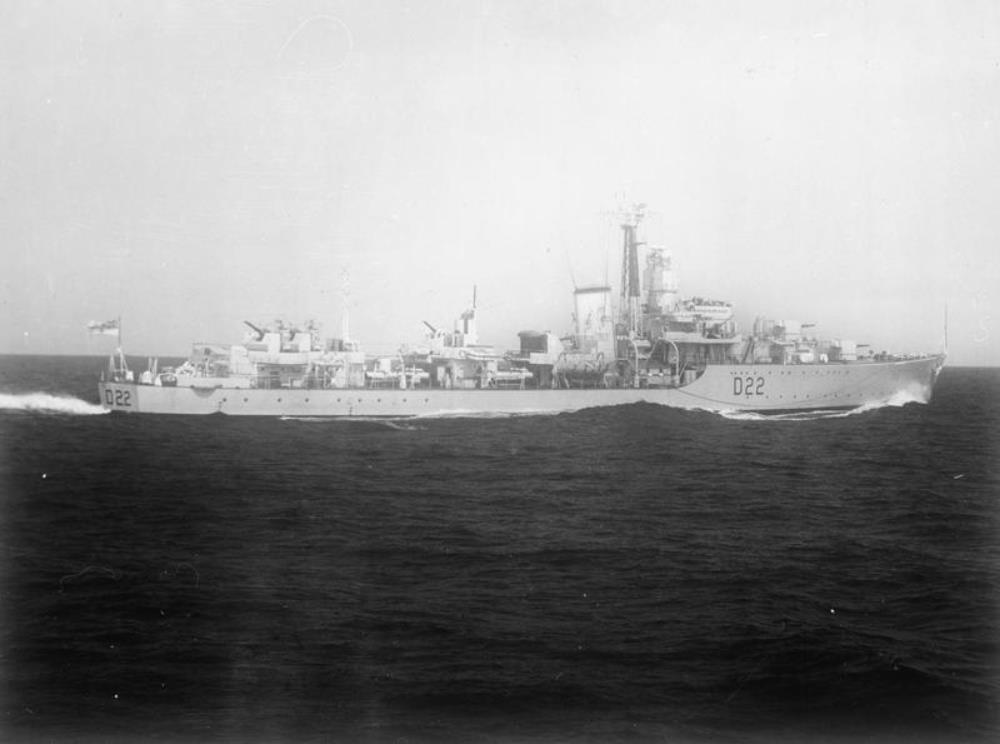 HMS Aisne
HMS Aisne
HMS Aisne – a Battle-class destroyer built by Vickers-Armstrongs, High Walker, launched 12th May 1945, (the first warship since VE Day), commissioned 20th March 1947.
Aisne joined the Home Fleet upon commission, but in 1950 she was temporarily laid-up. The following year, Aisne joined the 4th Destroyer Squadron, where she would subsequently have spells with the Home and Mediterranean Fleets
In 1954, Aisne, as part of the 4th Destroyer Squadron, deployed to the Mediterranean, remaining there until 1955. In 1959, Aisne was converted to a Radar Picket, extending her service life.
In 1962, Aisne she joined the 7th Destroyer Squadron, and the following year joined the 23rd Escort Squadron, and subsequently the 30th Escort Squadron, deployed to the Mediterranean in 1964, before deploying to join the Far East Fleet. In 1967, Aisne deployed to the West Indies remaining there until 1968, when she was decommissioned
She was sold to Thos. Ward, arriving at Inverkeithing in 1970.
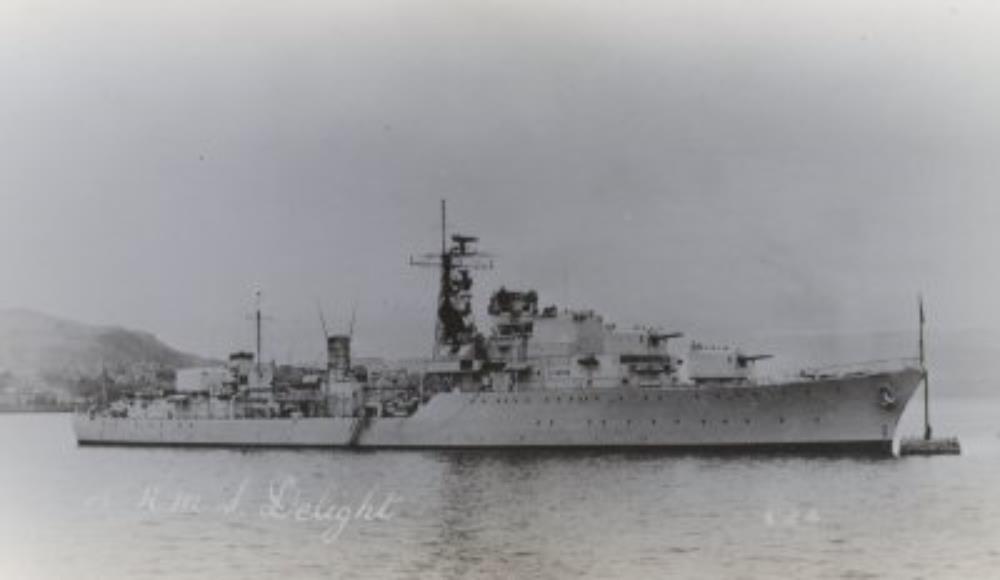 HMS Delight
HMS Delight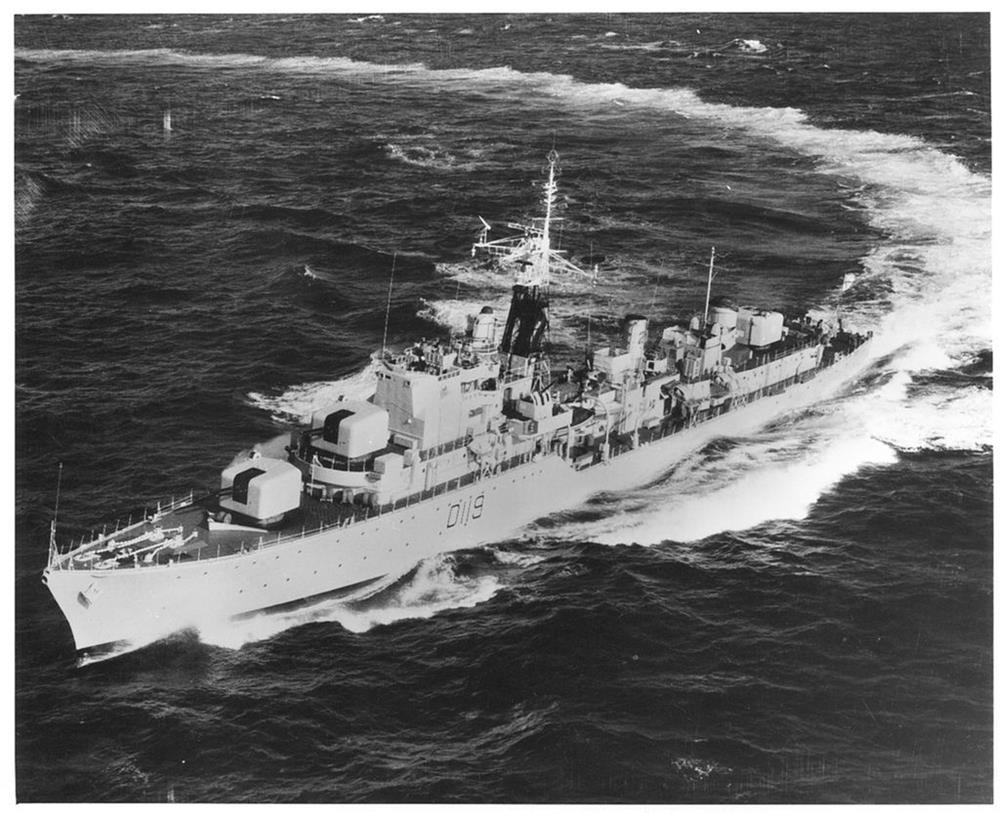 HMS Delight
HMS Delight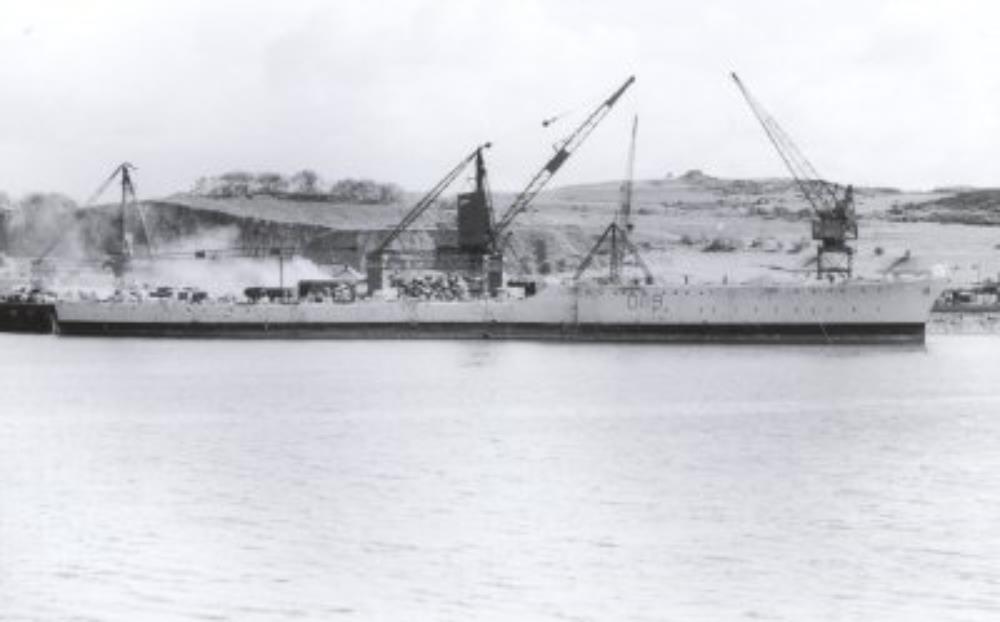 HMS Delight at Ward’s.
HMS Delight at Ward’s.
HMS Delight – a Daring-class destroyer, built by Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Govan, launched 21st December 1950.
In 1956 she formed part of the Royal Navy’s force used during the Suez Operation.
In 1959 Delight was involved in a collision in the Mediterranean with the cruiser Birmingham. Two ratings died during damage control activities.
Scrapped 1971
wikipedia
www.battleships-cruisers.co.uk
twitter.com
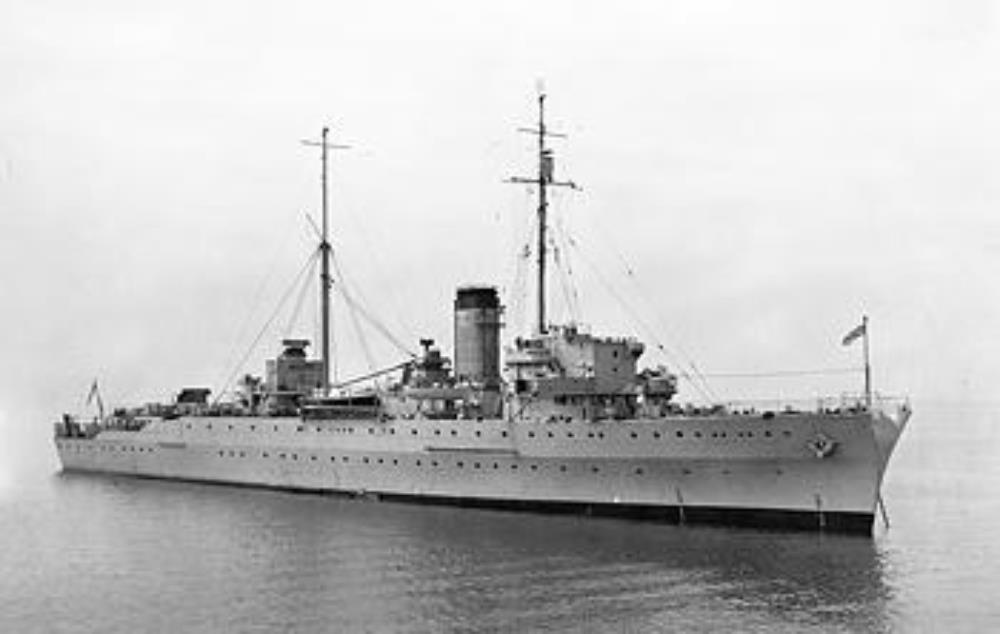 HMS Protector in 1952
HMS Protector in 1952
HMS Protector – a Fast net layer built by Yarrow Shipbuilders, Scotstoun, launched 20th August 1936, commissioned 30th December 1936.
Protector was part of the Mediterranean Fleet from February 1939. She served in the South Atlantic and the Norwegian Campaign during World War II before being hit by an aerial torpedo in the Mediterranean. She was towed to Bombay and repaired before returning to Britain after the end of hostilities.
Protector was modified in 1955 for service as a guard-ship for the Falkland Islands Dependencies and a survey vessel for Antarctic waters.
She made her first Antarctic patrol in the winter of 1955/56, serving the Falkland Islands and the British Antarctic Survey bases. She returned to the Antarctic 13 more times in her career. During her patrols the ship rescued the passengers and crew of the icebound MV Theron, including Sir Edmund Hillary and Dr Vivian Fuchs. In 1957, Protector rescued the passengers of the RRS Shackleton, which had struck an iceberg and had to perform emergency repairs to keep from sinking.
In 1960 Protector was under the command of the Commander in Chief, South Atlantic and South America.
Protector was sold for scrap at Inverkeithing on 10 February 1970. She was replaced by HMS Endurance.
Here is an account of her Antarctic voyage in 1964-65
| < 1962-1964 | Δ Index | 1971 > |