Naval ships broken at Wards 1949-1955
| < 1946-1948 | Δ Index | 1956-1961 > |

1949
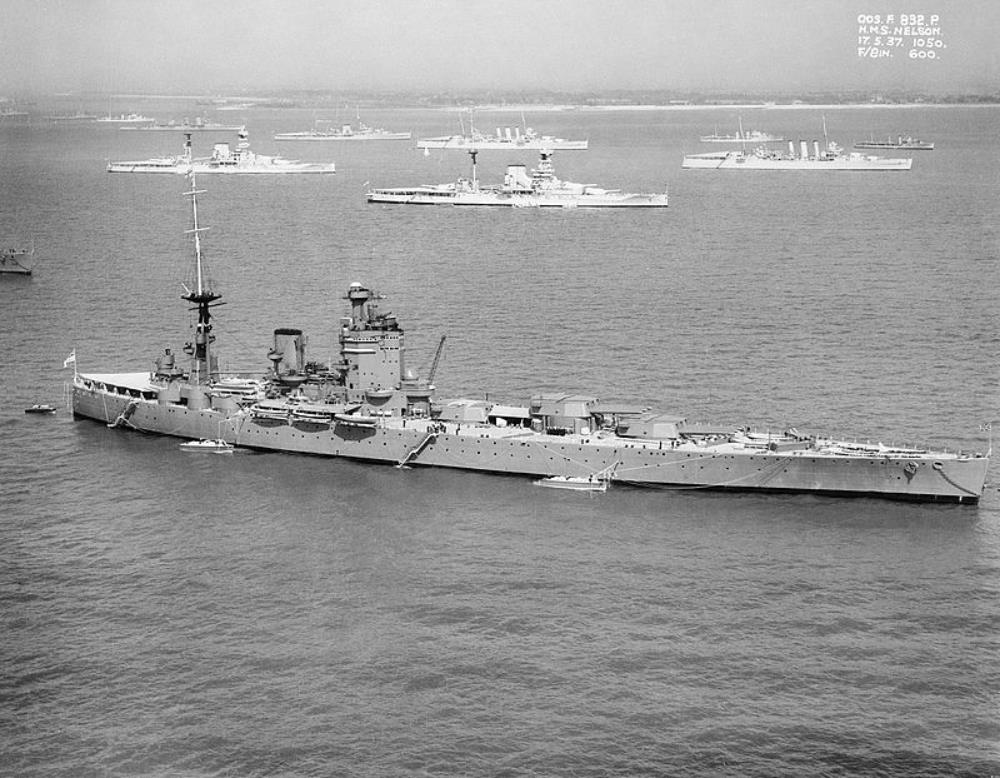 HMS Nelson
HMS Nelson
HMS Nelson – Nelson-class battleship, built by Armstrong-Whitworth, South Tyneside, launched 3rd September 1925, commissioned 15th August 1927.
The Nelson-class were the first battleships built to meet the limitations of the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922.
Entering service in 1927, the ship spent her peacetime career with the Atlantic and Home Fleets, usually as the fleet flagship. During the early stages of Second World War, she searched for German commerce raiders, missed participating in the Norwegian Campaign after she was badly damaged by a mine in late 1939, and escorted convoys in the Atlantic Ocean.
In mid-1941 Nelson escorted several convoys to Malta before being torpedoed in September. After repairs she resumed doing so before supporting the British invasion of French Algeria during Operation Torch in late 1942. The ship covered the invasions of Sicily (Operation Husky) and Italy (Operation Avalanche) in mid-1943 while bombarding coastal defences during Operation Baytown.
During the Normandy landings in June 1944, Nelson provided naval gunfire support before she struck a mine and spent the rest of the year under repair. The ship was transferred to the Eastern Fleet in mid-1945 and returned home a few months after the Japanese surrender in September to serve as the flagship of the Home Fleet.
She became a training ship in early 1946 and was reduced to reserve in late 1947. Nelson was scrapped two years later after being used as a target for bomb tests.
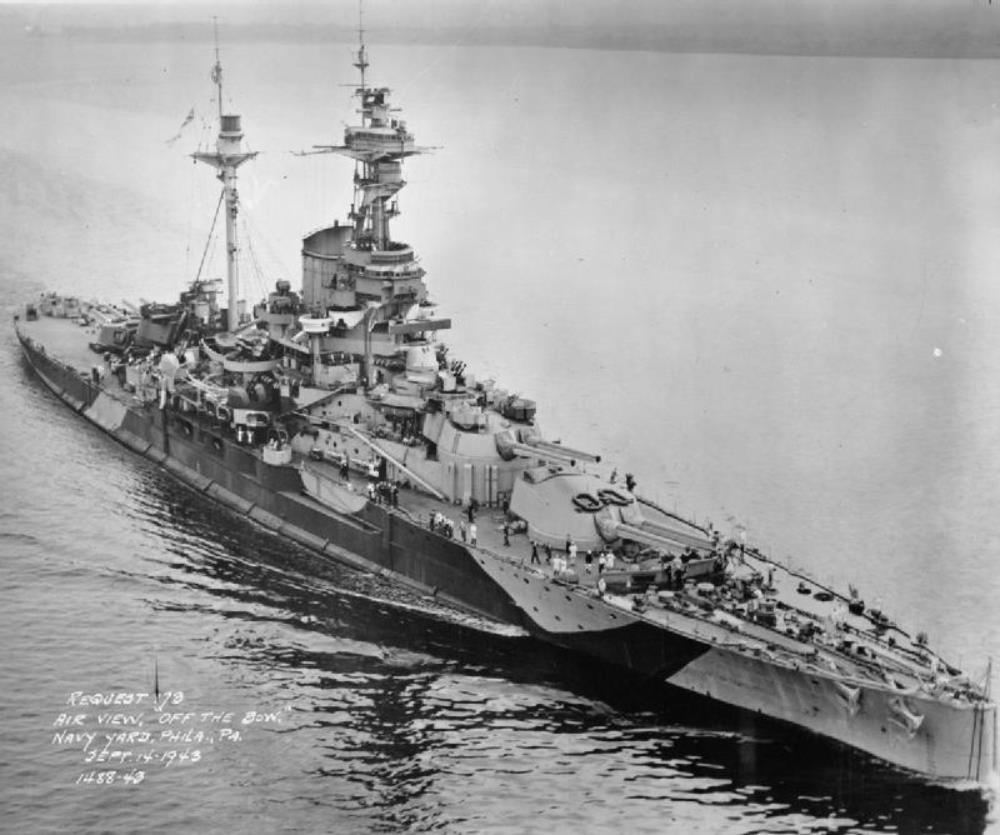 HMS Royal Sovereign
HMS Royal Sovereign
HMS Royal Sovereign – Revenge-class super-dreadnought battleship, built by HM Dockyard, Portsmouth, launched 29th April 1915, completed May 1916.
She served with the Grand Fleet during First World War, but did not see action (she was not ready for service for the Battle of Jutland in May 1916)
In the early 1930s, she was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet and based in Malta.
Unlike the Queen Elizabeth-class battleships, Royal Sovereign and her sisters were not modernised during the interwar period. Assigned to the Home Fleet, the ship was tasked with convoy protection until May 1940, when she returned to the Mediterranean Fleet. Royal Sovereign was present during the Battle of Calabria in July 1940, but her slow speed prevented her from engaging the Italian battleships.
By March 1942, she was assigned to the Eastern Fleet in the Indian Ocean, but after the Indian Ocean raid by Admiral Nagumo’s Kido Butai, the ship was withdrawn to eastern Africa to escort convoys.
In January 1944, she returned to Britain, and in May 1944 the Royal Navy transferred her to the Soviet Navy, which renamed her Arkhangelsk. She escorted Arctic convoys into Kola until the end of the war.
The Soviets returned the ship in 1949, after which she was broken up for scrap.
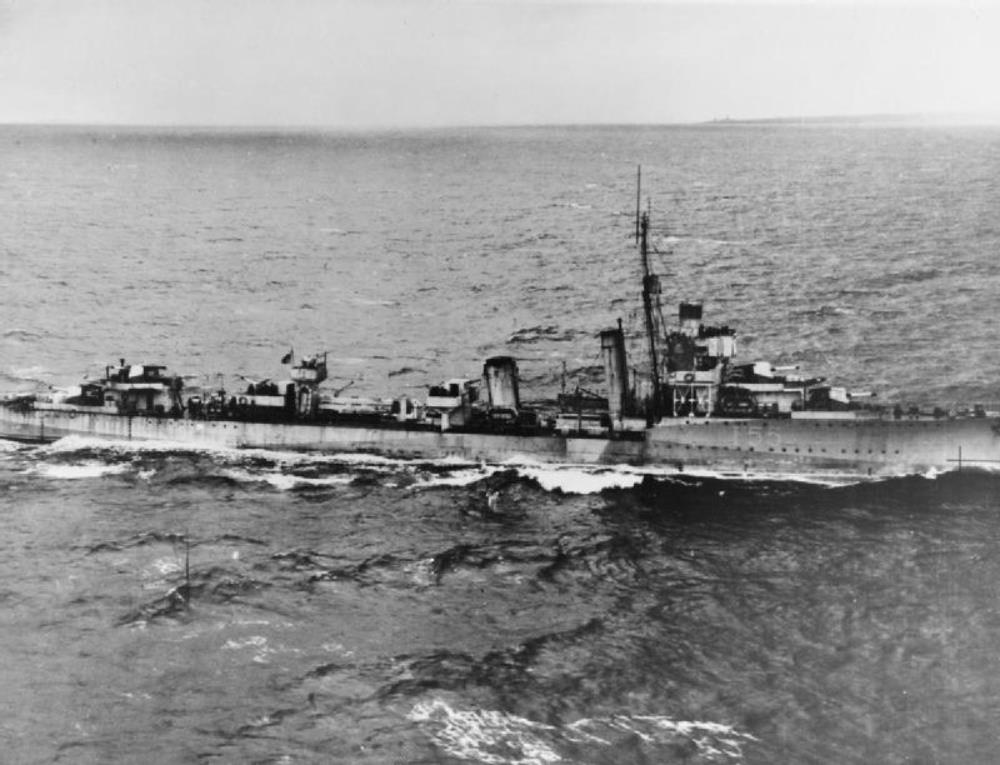 HMS Vesper
HMS Vesper
HMS Vesper – V-class destroyer built by Alexander Stephen and Sons, Glasgow, launched: 15th December 1917[, commissioned 20th February 1918
Vesper joined the fleet and remained in service during World War I, but was later decommissioned and placed in reserve.
She was recommissioned in 1939 and assigned to convoy defence and patrol duties in the Southwestern Approaches.
In May 1940, supported the evacuation of troops from France. She then provided anti-invasion patrol and convoy escort duties in the English Channel and North Sea, until December 1940, when she was assigned to duty in the Western Approaches. In December 1942, the Royal Navy selected Vesper for conversion to a “long-range escort,” for convoy escort duty in the North Atlantic Ocean and Western Approaches.
In April 1944, Vesper took part in Operation Neptune, the assault phase of the upcoming invasion of Normandy, , then served on convoy escort duty in the English Channel from July through September 1944, then operated on convoy defence duties in waters around the British Isles until the surrender of Germany in early May 1945.
She was sold to BISCO on 7 March 1947 for scrapping by Thos W Ward, and arrived at the shipbreaker’s yard in March 1948.
NSC (L)/9 – unknown
1950
HMS Albuera – a Battle-class destroyer ordered on 10 March 1943 from Vickers Armstrong on the Tyne. She was launched on 28 August 1945.
The order was cancelled on 15 October 1945 and she was sold incomplete for scrapping to Thos W Ward arriving at Inverkeithing on 21 November 1950
wikipedia
1952
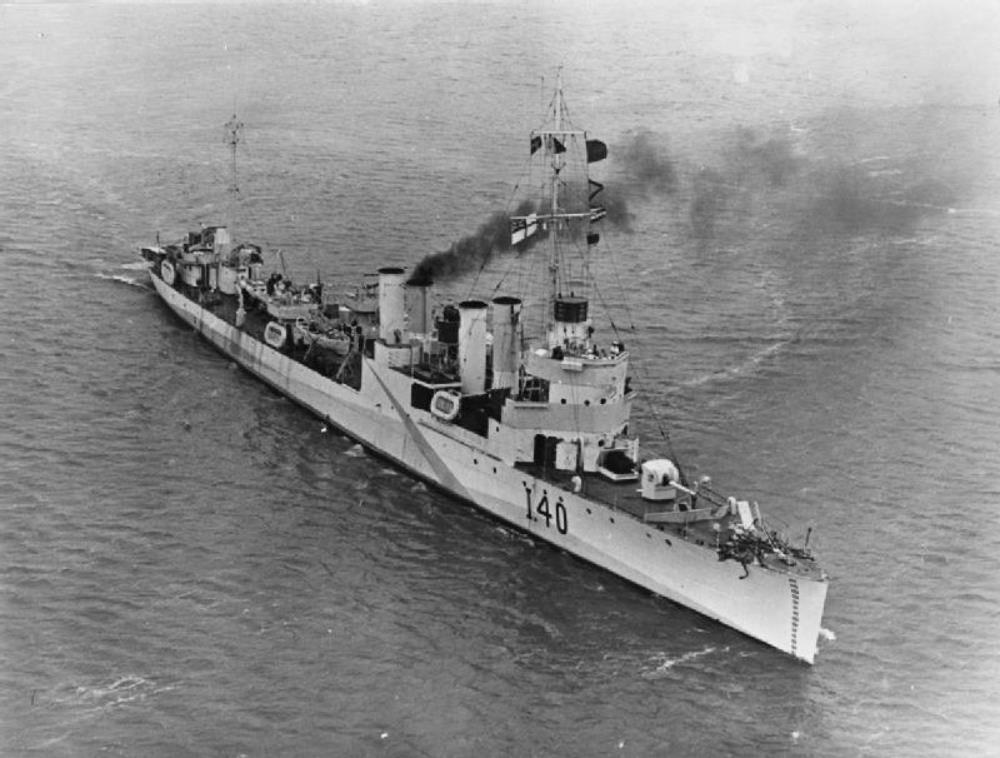 HMS Georgetown
HMS Georgetown
HMS Georgetown – began life as USS Maddox – US Navy Wickes-class destroyer built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company, Quincy, Massachusetts, launched 27th October 1918 commissioned 10th March 1919.
Assigned to Division 21, Atlantic Fleet, Maddox departed Boston 3 May 1919 for Trepassey, Newfoundland, en route to the Azores where she became part of a “bridge of ships” assigned to guide US Navy flying boats NC-1 and NC-4 across the ocean on the first transatlantic flight.
Returning to Boston on 22 May, the destroyer operated out of there until she sailed for Europe on 26 August 1919. Arriving at Brest, France on 19 September, she soon joined an honour escort for George Washington, then bound for Ostend, Belgium, to embark the Belgian King and Queen for the United States.
Detached on 25 September 1919, Maddox commenced cross-channel service. Until 24 October she escorted ships and carried naval and Army passengers from Dover and Harwich to Boulogne, France, and the Hook of Holland. Departing Harwich on 25 October, the four stacker proceeded through Kiel Canal to visit various Baltic ports.
Returning to the United States on 12 February 1920, Maddox operated out of Boston for the next 2 years, off the east coast. Departing Boston on 25 February 1922 for Philadelphia, she decommissioned at the Philadelphia Navy Yard on 14 June 1922.
Inactive for the next 18 years, Maddox recommissioned on 17 June 1940. After brief duty on mid-Atlantic Neutrality Patrol, she departed Newport, Rhode Island on 16 September 1940 for Halifax, Nova Scotia, where she decommissioned on 23 September 1940. The same day, under the destroyer-naval base agreement, she was transferred to Great Britain and commissioned in the Royal Navy as HMS Georgetown.
As Georgetown, she participated in operation “Bowery”, escorting the aircraft carrier Wasp in May 1942 on her second reinforcement of the Supermarine Spitfire strength on the island of Malta.
In September 1942, she transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy for convoy escort duties in the western Atlantic. Georgetown was modified for trade convoy escort service by removal of three of the original 4″/50 caliber guns and one of the triple torpedo tube mounts to reduce topside weight for additional depth charge stowage and installation of Hedgehog anti-submarine launcher.
Returned to the United Kingdom in December 1943, she joined the Reserve Fleet.
In August 1944 Georgetown was turned over to the Soviet Navy.
She was returned to the Royal Navy on 9 September 1952 and scrapped on 16 September 1952.
1953
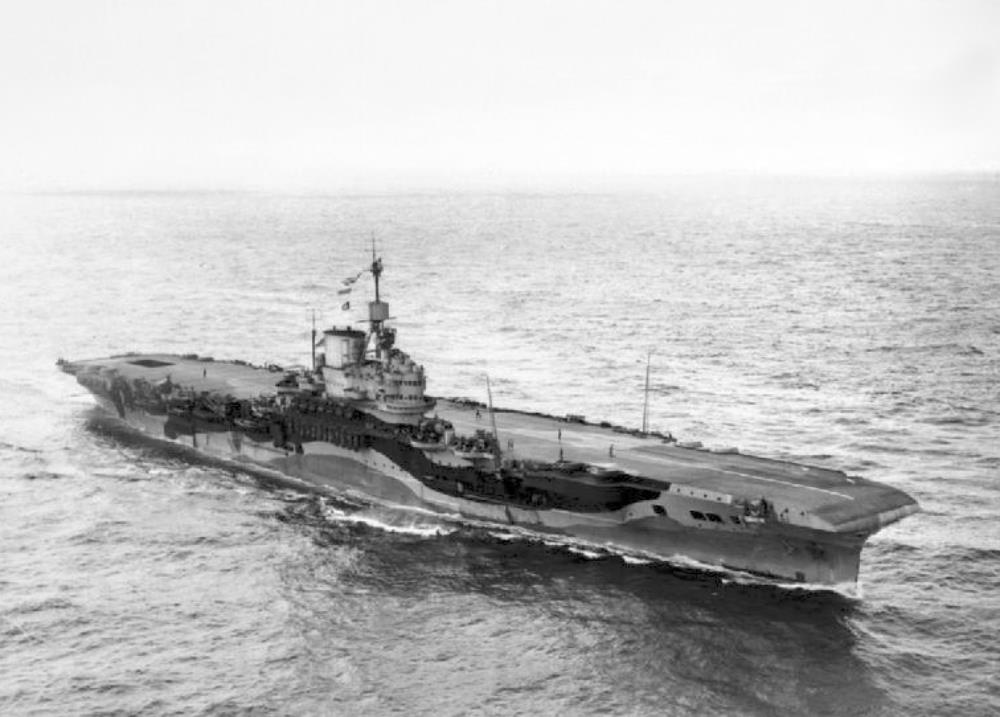 HMS Formidable
HMS Formidable
HMS Formidable – Illustrious-class Aircraft Carrier, built by Harland & Wolff, Belfast, launched 17th August 1939, commissioned 24th November 1940.
She was initially assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet, where her aircraft played a key role in the Battle of Cape Matapan in early 1941, subsequently providing cover for Allied ships and attacked Axis forces until the carrier was badly damaged by German dive bombers in May.
Formidable covered the invasion of Diego Suarez in Vichy Madagascar in early 1942, before participating in Operation Torch, the invasion of French North Africa in November. She remained in the Mediterranean and covered the invasions of Sicily and mainland Italy in 1943.
Formidable made several attacks on the German battleship Tirpitz in Norway in mid-1944. She was subsequently assigned to the British Pacific Fleet (BPF) in 1945 where she played a supporting role during the Battle of Okinawa and later attacked targets in the Japanese Home Islands. The ship was used to repatriate liberated Allied prisoners of war and soldiers after the Japanese surrender and then ferried British personnel across the globe through 1946.
She was placed in reserve the following year and sold for scrap in 1953.
1954
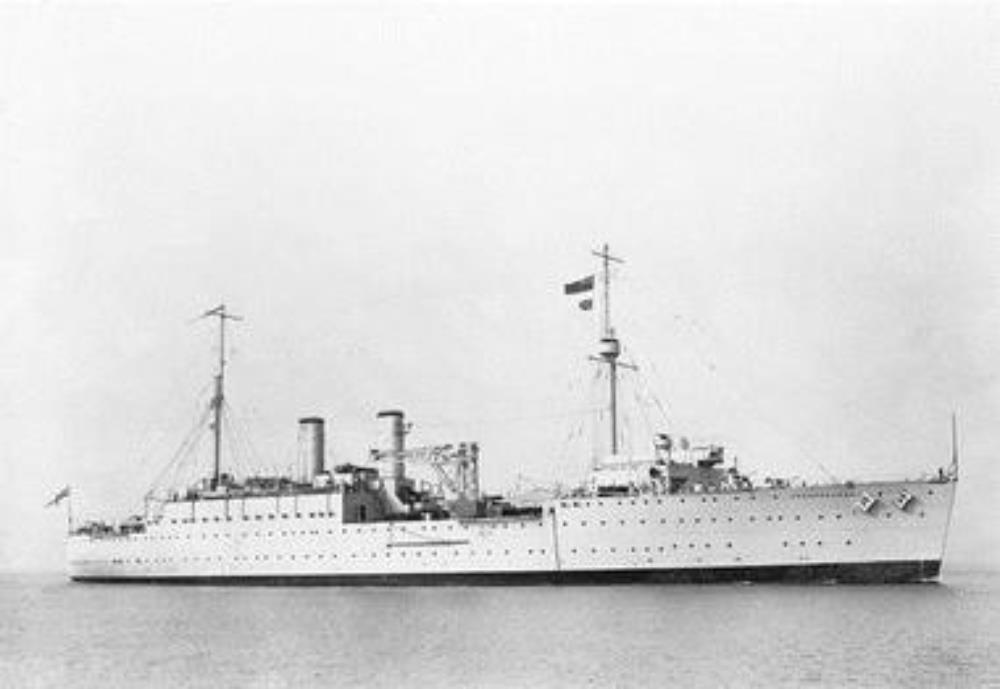 HMS Resource
HMS Resource
HMS Resource – Fleet repair ship built by Vickers-Armstrongs, Barrow-in-Furness, launched 27th November 1928.
She served in the Mediterranean from 1939 until 1944, except in early 1940 when she spent a small amount of time at Freetown. She served in the Eastern Fleet from 1944, and was scrapped at Inverkeithing in February 1954.
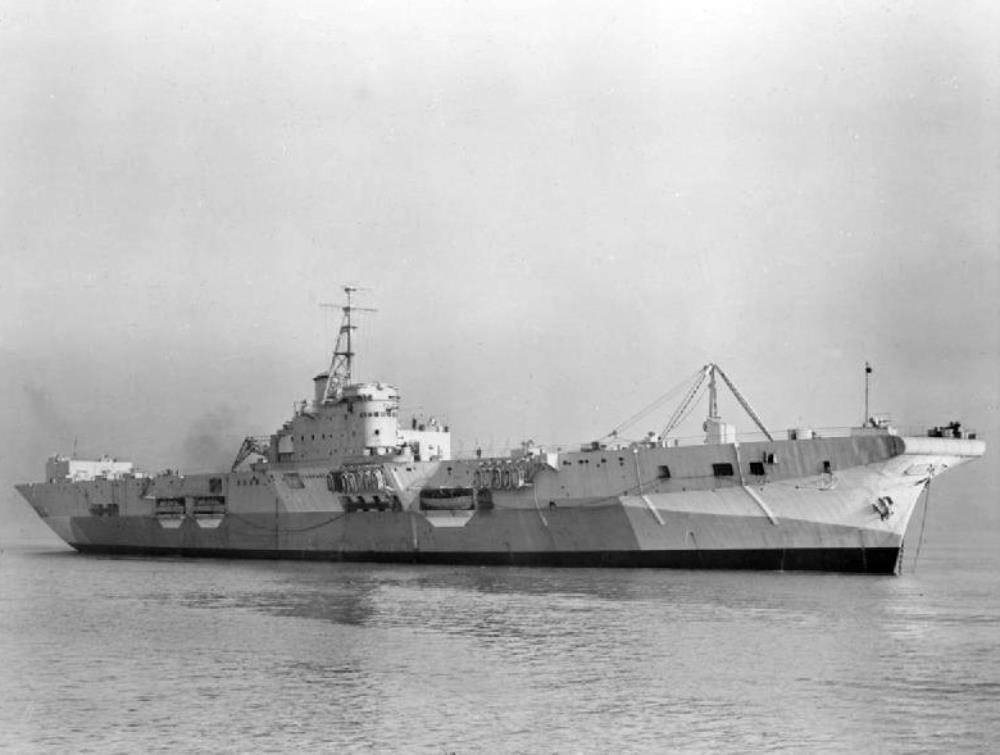 HMS Pioneer
HMS Pioneer
HMS Pioneer – Colossus-class aircraft carrier built by Vickers-Armstrong, Barrow-in-Furness launched 20th May 1944, completed 8th February 1945.
She was modified whilst under construction into an aircraft maintenance carrier.
The ship arrived in Australia in mid-1945 to support operations by the British Pacific Fleet against Japanese forces. She supported the British attacks on the Japanese Home Islands from mid-June until the end of the war in August from a base in the Admiralty Islands. The ship and her facilities were used to help repair Hong Kong’s infrastructure in late 1945 and she returned to the UK in early 1946.
Pioneer was immediately placed in reserve upon her arrival and she was sold in 1954 for scrap.
wikipedia
1955
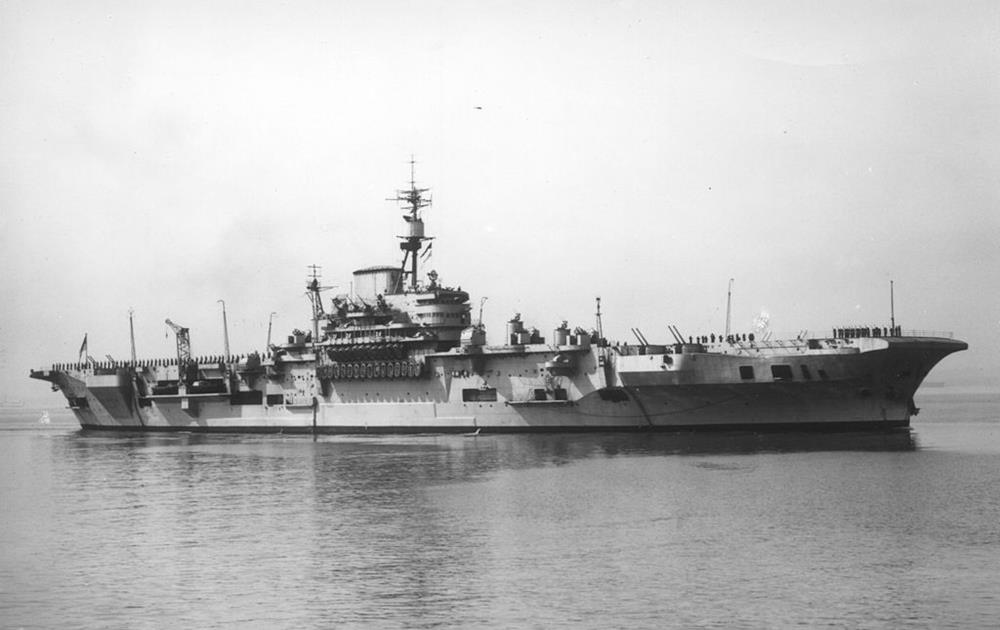 HMS Implacable
HMS Implacable
HMS Implacable – Implacable-class aircraft carrier built by Fairfield Shipbuilding, Govan launched 10th December 1942, commissioned 28th August 1944.
She was initially assigned to the Home Fleet and attacked targets in Norway for the rest of the year. She was subsequently assigned to the British Pacific Fleet (BPF) where she attacked the Japanese naval base at Truk and targets in the Japanese Home Islands in 1945. The ship was used to repatriate liberated Allied prisoners of war (PoWs) and soldiers after the Japanese surrender, for the rest of the year.
Implacable returned home in 1946 and became the Home Fleet’s deck-landing training carrier, a role that lasted until 1950. She briefly served as flagship of the Home Fleet in 1950. During this time she participated in many exercises and made a number of port visits in Western Europe.
She was placed in reserve in 1950 and converted into a training ship in 1952, and served as flagship of the Home Fleet Training Squadron. The ship was considered for a major modernisation in 1951–52, but this was rejected as too expensive and time-consuming. Implacable was decommissioned in 1954 and sold for scrap in 1955.
| < 1946-1948 | Δ Index | 1956-1961 > |